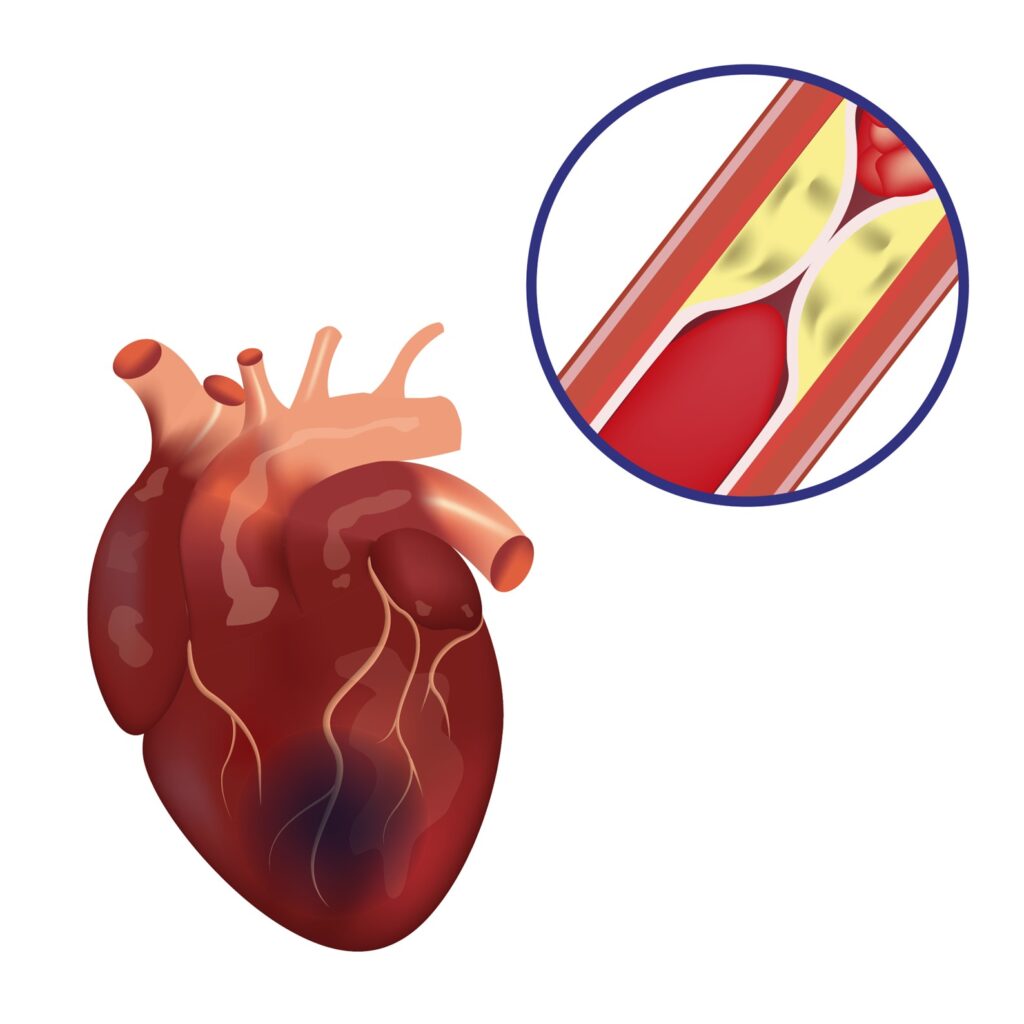
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition that affects the coronary arteries, which are responsible for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. This condition occurs when the arteries become narrow or blocked due to the buildup of plaque, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms
• Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
• Shortness of breath
• Nausea or dizziness
• Pain or discomfort in the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back
Causes
• Buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries
• High blood pressure
• High cholesterol levels
• Smoking
• Diabetes
• Obesity
• Lack of physical activity
• Family history of CAD
Risk factors
• Age (risk increases after age 45 for men and after age 55 for women)
• Gender (men are at higher risk than women)
• Family history of CAD
• Smoking
• High blood pressure
• High cholesterol levels
• Diabetes
• Obesity
• Lack of physical activity
• Stress
To prevent CAD, it is important to make lifestyle changes such as:
• Quitting smoking
• Maintaining a healthy weight
• Eating a heart-healthy diet
• Exercising regularly
• Managing stress
• Managing underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes
Diagnosis tests
• Electrocardiogram (ECG)
• Stress test
• Echocardiogram
• Cardiac catheterization
Treatment
• Lifestyle changes
• Medications such as aspirin, beta-blockers, and cholesterol-lowering drugs
• Medical procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement
• Surgery such as bypass surgery
Myth and fact
• Myth: Only older people get CAD.
• Fact: CAD can affect people of any age, including children and young adults.
Patient FAQs
Can CAD be cured?
While CAD cannot be cured, it can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
What is the best diet for preventing CAD?
A heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is recommended.
Can stress cause CAD?
While stress is not a direct cause of CAD, it can contribute to the development of risk factors such as high blood pressure and unhealthy coping behaviors such as smoking and overeating.
In conclusion, CAD is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. By making lifestyle changes and managing underlying health conditions, it is possible to reduce the risk of CAD and improve overall heart health.